Patterson & Kurtz (2020) Comparison-based learning of relational categories (you'll never guess)
Abstract
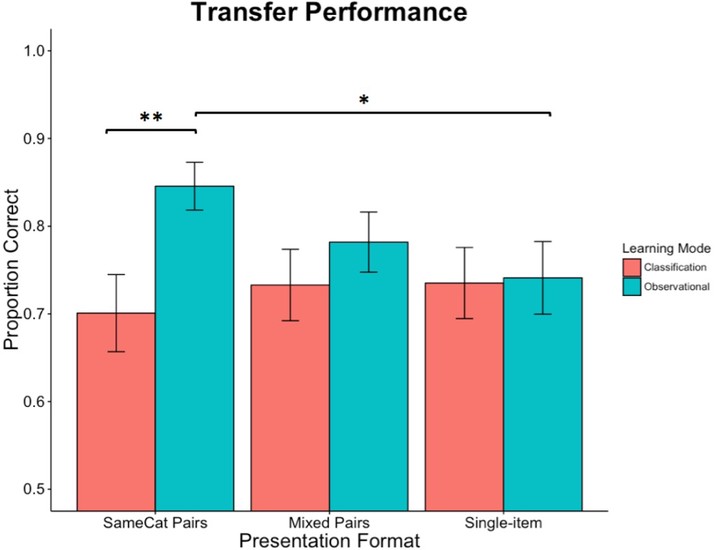
In accord with structural alignment theory, same-category comparison opportunities within a classification learning task should promote relational category acquisition. However, a straightforward merging of the classification paradigm with co-presentation of same-category item pairs does not yield an advantage relative to an equal number of single-item exposures. In three experiments, we explore the hypothesis that the traditional classification learning mode (guess-and-correct) and comparison have a previously unforeseen incompatibility. In Experiment 1, we test this hypothesis by contrasting classification with supervised observational learning (passive study of labeled examples) under three presentation formats: same-category pairs, mixed pairs, and single-item. We find an observational advantage with same-category pairs and produce the elusive advantage over single-item exposures. In Experiment 2, we assess the generality of the learning mode effect by testing both same- and different-category comparison. The observational advantage replicates and extends to different-category comparison – although, we do not find a significant difference between the two types of comparison. In Experiment 3, relative to the classification mode, we find enhanced performance in an intermediate learning mode between classification and observation in which participants are instructed to make a covert category guess (without making an actual response) before seeing the correct category label. Implications and interpretations – including our interpretation that the performance emphasis inherent in classification learning undermines the benefits that arise from comparison opportunities – are discussed.